
Finally, 22 patients were identified and included in this study.
We retrospectively analyzed the data of all patients. Between March 2015 and October 2018, we treated 167 ankle fractures involving the distal tibial plafond at 1 regional level-1 trauma center. The present study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital, and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
#Distal tibia fibula fracture series#
The purpose of the present study was to describe the approach in detail and to present a series of patients with clinical and radiographic outcomes. Then, we employed a novel approach that provided direct visualization of the fibular notch to treat specific ankle fractures. Inspired by ankle arthrodesis via the transfibular approach, we hypothesized that utilizing the broken lateral structure injured in the original injury could provide ideal visualization of the articular fragments, especially the articular surface, to facilitate the reduction of some complex fractures.
#Distal tibia fibula fracture skin#
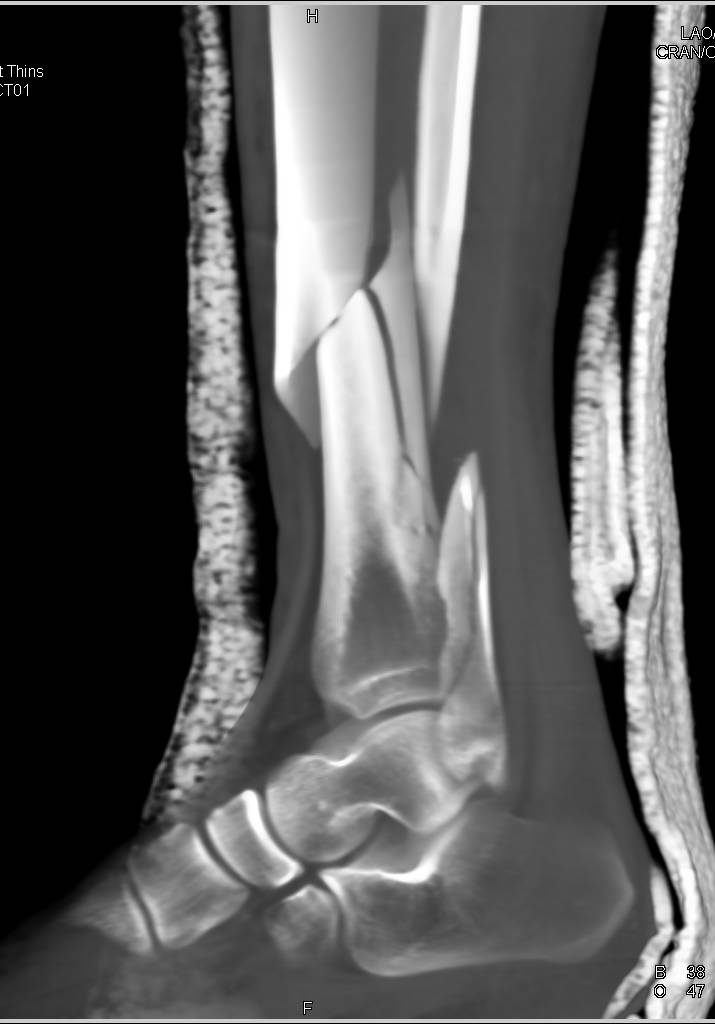
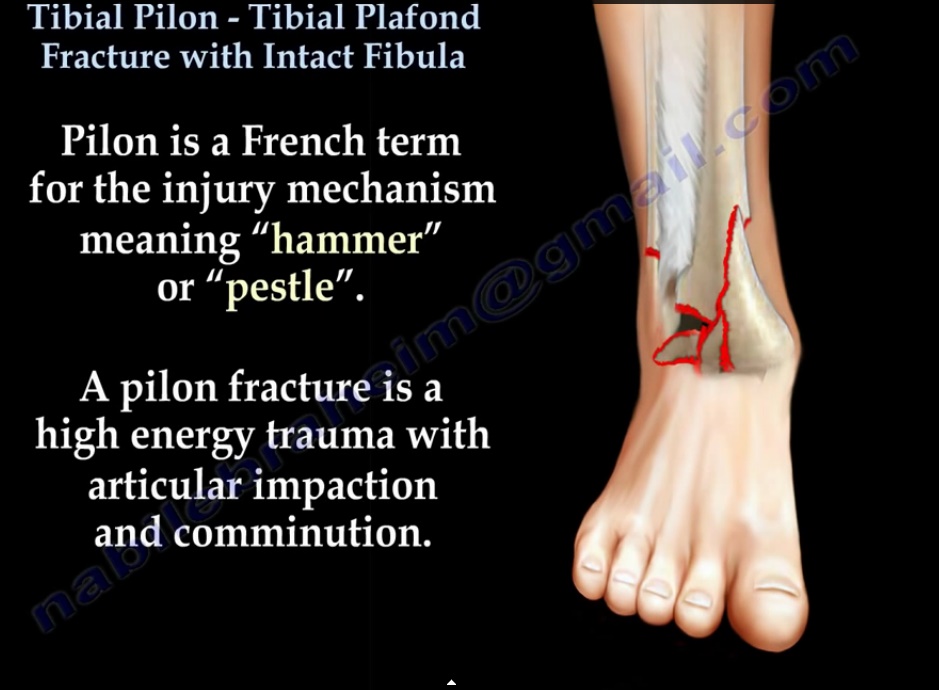
In such fractures, a conventional single incision is usually insufficient for direct visualization of the articular fragments, especially the whole articular surface, while a more visible combined incision carries an increased risk of narrow skin bridge necrosis. Sometimes, they are characterized by concomitant fibular fracture and distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. Typically, severe ankle fractures (AO/OTA type 44) and distal tibial plafond fractures (AO/OTA type 43) are caused by combined axial load and valgus or rotational force. For ease of fracture reduction, a variety of surgical incisions have been employed in the treatment of various ankle fractures. Īlthough efficacy is related to many factors, the surgical approach is one of the most important intervention factors for complex distal tibial fractures. Orthopedic surgeons have been striving for ideal results however, posttraumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA) and soft tissue-related complications have been bothersome to patients and surgeons, especially when there are comminuted articular fragments. Anatomical reduction of articular fragments and restoration of normal alignment as well as ankle stability have been considered to be the keys to success. Satisfactory radiographic and clinical results were observed, and further clinical and anatomical studies are recommended to ascertain the feasibility of this approach in the treatment of complex distal tibial fractures.Īnkle fractures involving the distal tibial plafond, including traditional pilon fractures and atypical ankle fractures, are usually the result of combined axial load and shear force. This approach provides excellent direct visualization of the fragments and articular surface without significantly increasing iatrogenic injuries. The fibular notch approach is a safe and reliable approach for the treatment of specific ankle fractures involving the distal tibial plafond. The average AOFAS score was 88.8 at the last follow-up. Mild posttraumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA) was present in 4 patients. All fractures healed with an average time of 17.3 ± 3.6 weeks. Postoperative radiography revealed satisfying restoration of all fractures and syndesmosis. ResultsĪll surgeries were successfully performed via the fibular notch approach as the primary approach with excellent intraoperative visualization.

The American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society Ankle-Hindfoot Scale (AOFAS) score was implemented for clinical functional assessment. The quality of fractures and syndesmosis reduction was examined using CT scans, and lateral stability of the ankle was assessed by physical examination and stress radiographs.

Relevant data were reviewed from the medical records. The details of the surgical technique were reviewed from the operative notes. Twenty-two patients with distal tibial plafond fractures with concomitant fibular and distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries were treated through a fibular notch approach in this retrospective study. Here, we present an innovative fibular notch approach for the treatment of some specific ankle fractures and present a series of patients with either functional or radiographic outcomes. Ankle fractures involving the distal tibial plafond frequently present a surgical challenge in choosing which incisions will be best for surgical treatment. Although efficacy is related to many factors, the surgical approach is one of the most important intervention factors for complex ankle fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
